UPS Launching On-Demand 3D Printing Manufacturing Network
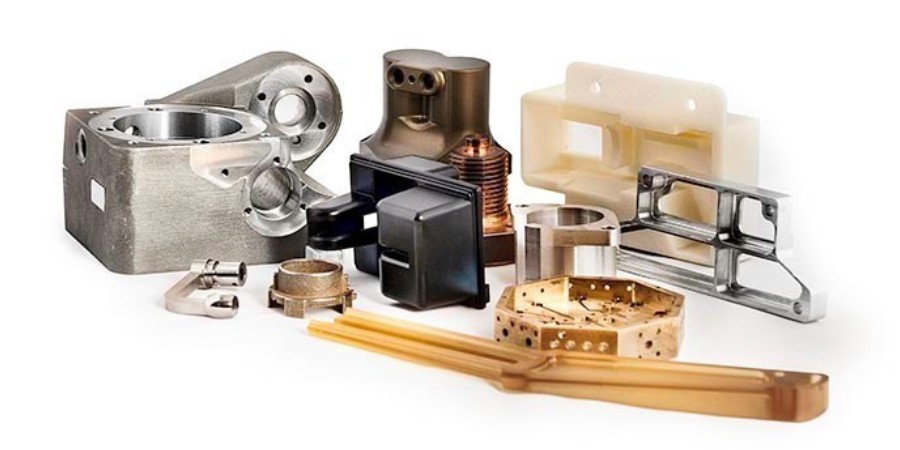
UPS will launch a distributed, on-demand manufacturing network that links its global logistics network with 3D printers at The UPS Store in more than 60 locations around the U.S. and Fast Radius’ On Demand Production Platform and 3D printing factory in Louisville, Kentucky. The integration into one additive manufacturing and logistics solution this summer will make 3D printing accessible to more potential users, enabling them to realize the convenience and cost-savings this technology offers.
Further strengthening UPS’s distributed, on-demand manufacturing offering, SAP today announced an agreement with UPS to create an end-to-end industrial solution. SAP’s extended supply chain solutions will be integrated with UPS’s on-demand manufacturing solution and global logistics network to simplify the industrial manufacturing process from digitization, certification, order-to-manufacturing and delivery.SAP made its announcement at the SAPPHIRE NOW conference.
“UPS is a leader in bringing industrial-strength 3D printing to reality. By building this disruptive technology into our supply chain models, we also bring new value to our manufacturing customers of all sizes,” said Stan Deans, president, UPS Global Distribution & Logistics. “Additive manufacturing technology is still developing rapidly so ‘manufacturing as a service’ is a smart approach for many companies.”
Customers will visit the Fast Radius website (formerly CloudDDM) to place their 3D printing orders, which will be directed to the optimal manufacturing or The UPS Store location based on speed, geography, and the product quality the customer requires. Orders can be shipped as early as same day. While participating The UPS Store locations are all in the U.S., companies globally could utilize the network and place orders.
By integrating SAP’s extended supply chain software with the UPS additive manufacturing solution and logistics network, manufacturing companies of all sizes will be able to access on-demand industrial manufacturing with the touch of a button. SAP customers will be able to digitize and simplify the production part approval process through SAP and their orders can be seamlessly routed to UPS for production and delivery.
The on-demand network created will benefit customers of all sizes:
- Manufacturers wanting to reduce inventory for slow-moving parts
- Manufacturers with short production runs where the cost to create the mold or tooling could make these orders too expensive for traditional manufacturing
- Manufacturers and retailers of custom/semi-custom goods as additive manufacturing allows cost-effective customization of goods
- Industrial designers and engineers who want high quality rapid prototypes delivered as fast as one day
- Entrepreneurs, start-ups and manufacturers who don’t currently have access to 3D printers or have limited capital and time and will use 3D printing for rapid prototyping and manufacturing of initial production runs
“Fast Radius plans to continue enhancing its production platform and to globally expand its manufacturing capabilities in 3D printing (plastics and metals), CNC machining and rapid injection molding,”said Rick Smith, co-founder and CEO of Fast Radius. “With this distributed, on-demand manufacturing network, UPS customers will be able to get their products to market faster and more cost-effectively because parts can be produced exactly in the quantity they need and when they need them. The potential of on-demand manufacturing is here today.”
The UPS Store was the the first nationwide retailer to offer 3D printing services in-store. “Connecting all The UPS Store locations into a larger network provides more opportunity for new customers to access our printers and gives customers added flexibility to match their requirements with the appropriate UPS location,” said Daniel Remba, Small Business Technology Leader for The UPS Store, Inc.
For more information about 3D printing at UPS, please visit www.ups.com/3Dprinting. UPS is a minority investor in Fast Radius through the UPS Strategic Enterprise Fund (SEF). The UPS SEF is a corporate venture capital group that focuses on developing critical partnerships and acquiring knowledge returns from its investments in information technology companies and emerging market-spaces.
UPS Launching On-Demand 3D Printing Manufacturing Network Read More »