News from Abroad: Safer Technologies and Carbon Cutting
Today’s News from Abroad installment highlights more carbon-cutting trends from the steel industry, ranging from robots in the cast house to recycling best practices.
Heat Treat Today partners with two international publications to deliver the latest news, tech tips, and cutting-edge articles that will serve our audience — manufacturers with in-house heat treat. heat processing, a Vulkan-Verlag GmbH publication, serves mostly the European and Asian heat treat markets, and Furnaces International, a Quartz Business Media publication. primarilyserves the English-speaking globe.
Robots Bring Safety to Casting
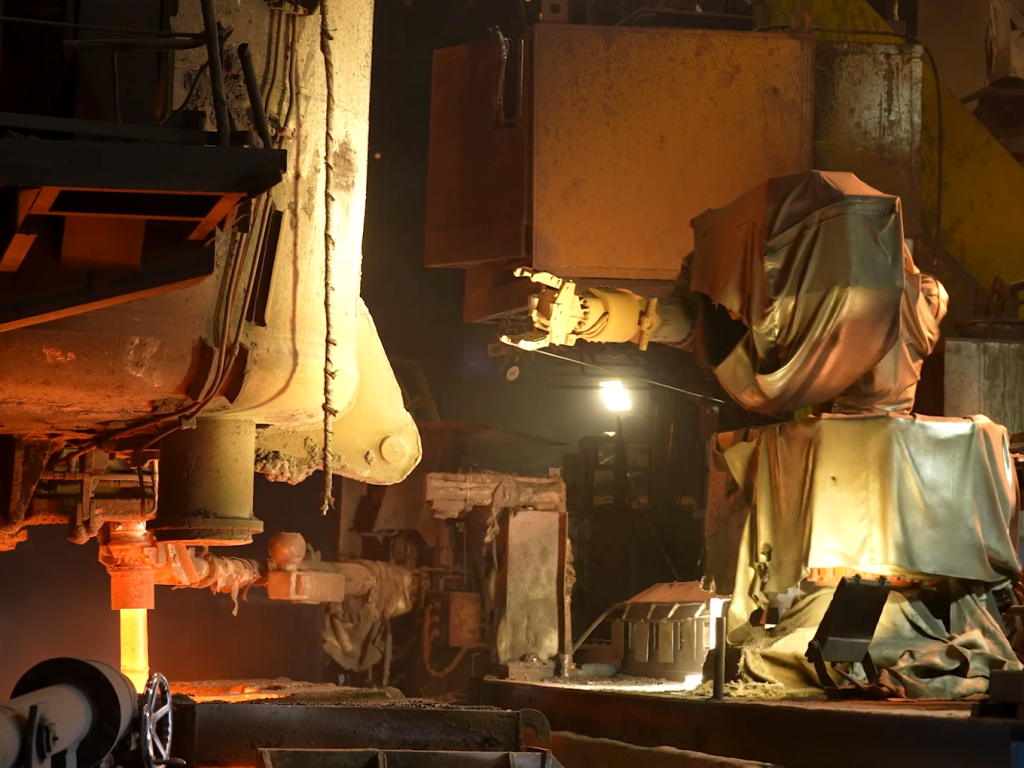

“Thai steel producer Siam Yamato Steel has implemented a new robot concept from Primetals Technologies, including LiquiRob, at its steelworks in Map Ta Phut . . .. Thanks to the robotics solution, safety and occupational health in the steelworks have significantly improved. Previously, workers who manually operated the shadow tube had to stand directly next to the distributor and the stream of steel flowing out of the ladle. In the case of a so-called ‘frozen pan.’”
READ MORE: “Primetals Technologies: New robotics concept for safer casting processes” at heat-processing.com
Carbon Cut with Induction Solution at High Heats
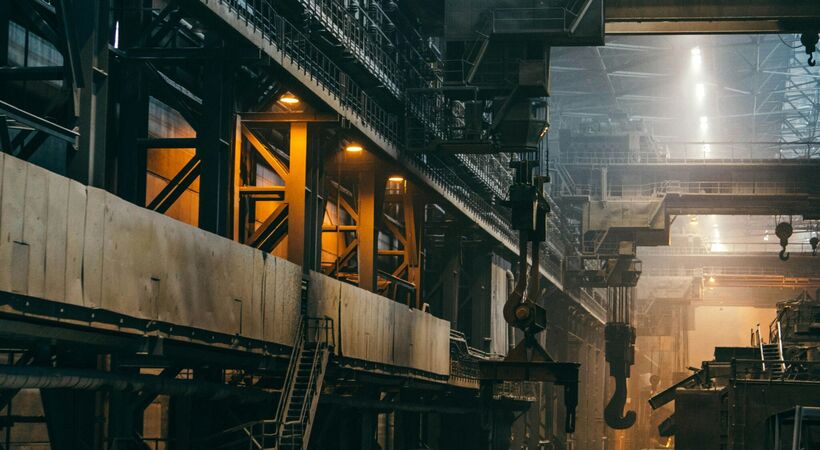

“Nippon Steel Stainless Steel Corporation and Sojitz Group met with our induction team at Fives headquarters in Paris for a detailed design review of the transverse flux induction heating system. CELES EcoTransFlux™ is an induction heating technology with very high heating rates at extremely high temperatures, and a compact footprint. It also has a minimal environmental footprint, making it beneficial for steelmakers to improve their carbon, stainless or electrical steel production.”
READ MORE: “Breakthrough technology for steelmakers” at furnaces-international.com
Standards To Maximize Can Recyclability
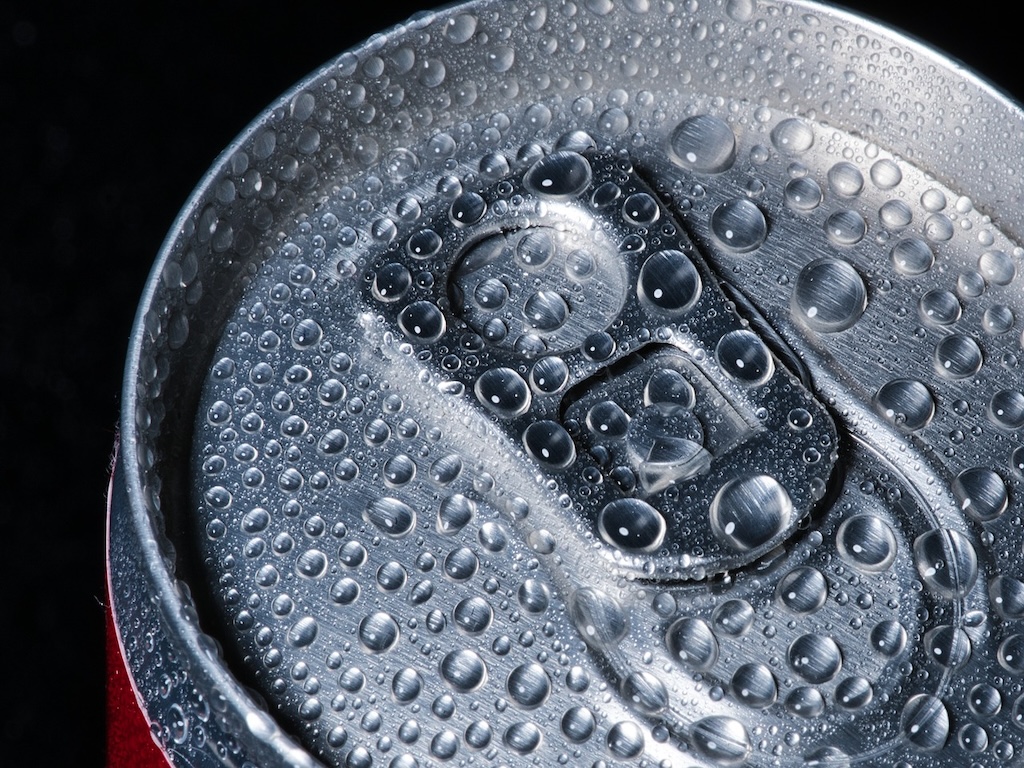

“Four leading flat-rolled aluminium manufacturers and members of the European Aluminium Packaging Group (EAPG), Constellium, Elval, Novelis and Speira, have signed an agreement to engage in a standardisation project to maximise the recycled content levels of the beverage can and thus substantially lower carbon emissions, focused on increased recyclability of the can end.”
READ MORE: “European Aluminium Producers Agree on Standardisation Project for Cans” at heat-processing.com
Mini-Mill Investment Transforms Future for Swedish Metal Manufacturer
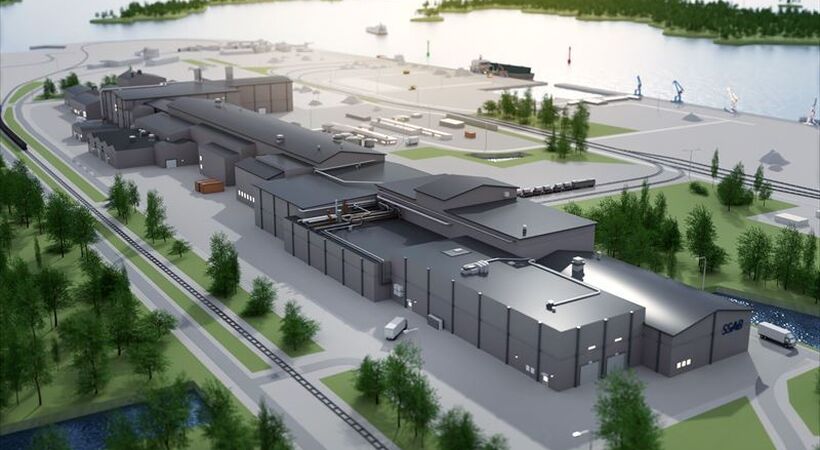

“SSAB’s Board of Directors have taken the decision to proceed with the next step in SSABs transition, building a state-of-the-art fossil-free mini-mill in Luleå, Sweden. When completed SSAB will close the current blast furnace-based production system. This will reduce Sweden’s CO2 emissions with 7% in addition to the 3% from the Oxelösund mill conversion.”
READ MORE: SSAB continues the transformation with a fossil-free mini-mill in Luleå, Sweden” at furnaces-international.com
Find Heat Treating Products And Services When You Search On Heat Treat Buyers Guide.Com
News from Abroad: Safer Technologies and Carbon Cutting Read More »