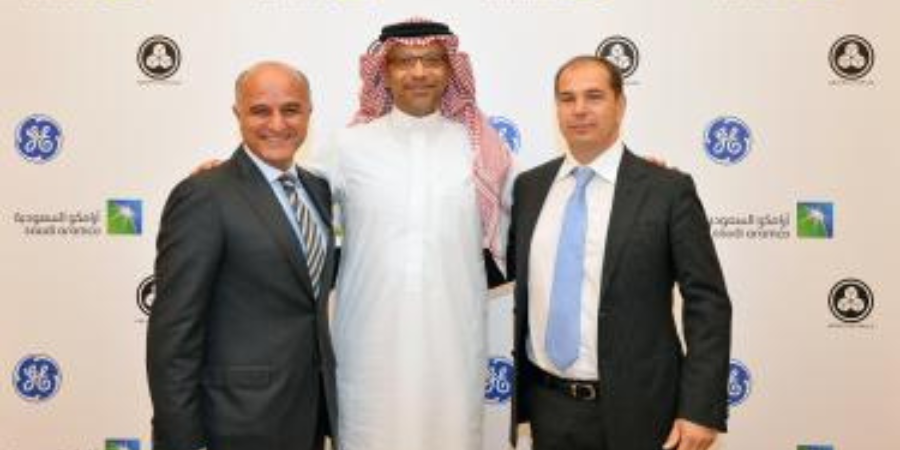
Saudi Aramco has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with GE (NYSE: GE) and Cividale SpA of Italy to build the Middle East and North Africa’s first-of-its-kind high-end forging & casting manufacturing facility that will serve the region’s maritime and energy industries.
Marking a joint investment of over US$400 million (SAR1.5 billion), the new facility, to be located in Ras Al-Khair under the Royal Commission of Jubail and Yanbu industrial area, aims to establish a high-value supply chain that boosts exports and economic competitiveness. Set to be operational in 2020, the plant will create 2,000 quality jobs in the Kingdom and catalyze the growth of Saudi small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
The MoU follows a preliminary partnership between Saudi Aramco and Cividale, a leading European producer in the steel and cast iron sector, to conduct feasibility studies for forging and casting manufacturing services in the Kingdom. GE has come on board to extend its expertise and investment in developing the world-class manufacturing plant through a joint venture between the three entities.
The Forging & Casting Manufacturing Facility complements plans by Saudi Aramco to develop several industrial projects in the Kingdom including a maritime project focused on building, maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO) of offshore platforms, jack-ups, offshore service vessels and commercial tankers.
Saudi Aramco is also working with its partners to develop an onshore rig manufacturing facility for providing new build and MRO services to onshore rigs and systems; an engine manufacturing project for the manufacturing, maintenance and repair of diesel engines, manufacturing and repair of marine pumps; and an Energy Industrial City to accelerate manufacturing industries in the oil and gas sector.
The Forging & Casting Manufacturing Facility will serve all these projects in addition to providing the best-in-class services and technologies to downstream & other industries across the region and global markets. It will also support the ongoing emphasis of the government, under Saudi Vision 2030, to develop the mining sector of the Kingdom by creating a domestic source-market for various raw materials & supplies that go into the production line.
Abdallah I. Al-Saadan, Senior Vice President, Finance, Strategy & Development, Saudi Aramco, said: “The MoU reflects our ambition to create a robust supply chain that builds positive synergies in the oil and gas manufacturing sector. This builds on our deep commitment to support the goals of Saudi Vision 2030 to promote economic and industrial diversification in the Kingdom and boost localized manufacturing.”
Rami Qasem, President & CEO, GE Oil & Gas, Middle East, North Africa & Turkey said: “For the Forging & Casting Manufacturing Facility, we will leverage our already strong expertise in ‘Made in Saudi’ manufacturing. Together with our partners, we will actively engage Saudi SMEs to support the plant’s operations, and train & hire Saudi professionals, adding further value to the economy. By building a domestic forging and casting production unit, Saudi and regional customers can achieve greater operational efficiencies in product procurement, repair and service support.”
Antonio Valduga, President of Cividale, added: “The feasibility assessment study underlines the strong potential for a world-class manufacturing facility for forging and casting services in the Kingdom. Developing a full-fledged facility through the joint partnership will position Saudi Arabia as a technology and services hub for specialized equipment and services.”
The collaboration is a strong example of the public-private partnerships that the government fosters under Saudi Vision 2030 to develop local manufacturing capabilities that add significant value to the economy.
![]() Source: Total Materia
Source: Total Materia